MySQL内部临时表的具体使用
目录
- union
- 表初始化
- 执行语句
- union result
- union all
- group by
- 内存充足
- 执行语句
- 执行过程
- 排序过程
- order by null
- 内存不足
- 执行语句
- 优化方案
- 优化索引
- 直接排序
- 执行过程
- 对比distinct
- 小结
- 参考资料
union
union语义:取两个子查询结果的并集,重复的行只保留一行
表初始化
?| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 | create table t1(id int primary key , a int , b int , index (a)); delimiter ;; create procedure idata() begin declare i int ; set i=1; while (i<= 1000) do insert into t1 values (i,i,i); set i=i+1; end while; end ;; delimiter ; call idata(); |
执行语句
?| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | ( select 1000 as f) union ( select id from t1 order by id desc limit 2); mysql> explain ( select 1000 as f) union ( select id from t1 order by id desc limit 2); + ----+--------------+------------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | extra | + ----+--------------+------------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------+ | 1 | primary | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | no tables used | | 2 | union | t1 | null | index | null | primary | 4 | null | 2 | 100.00 | backward index scan; using index | | null | union result | <union1,2> | null | all | null | null | null | null | null | null | using temporary | + ----+--------------+------------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------+ |
第二行的key=primary,using temporary
- 表示在对子查询的结果做
union result的时候,使用了临时表
union result
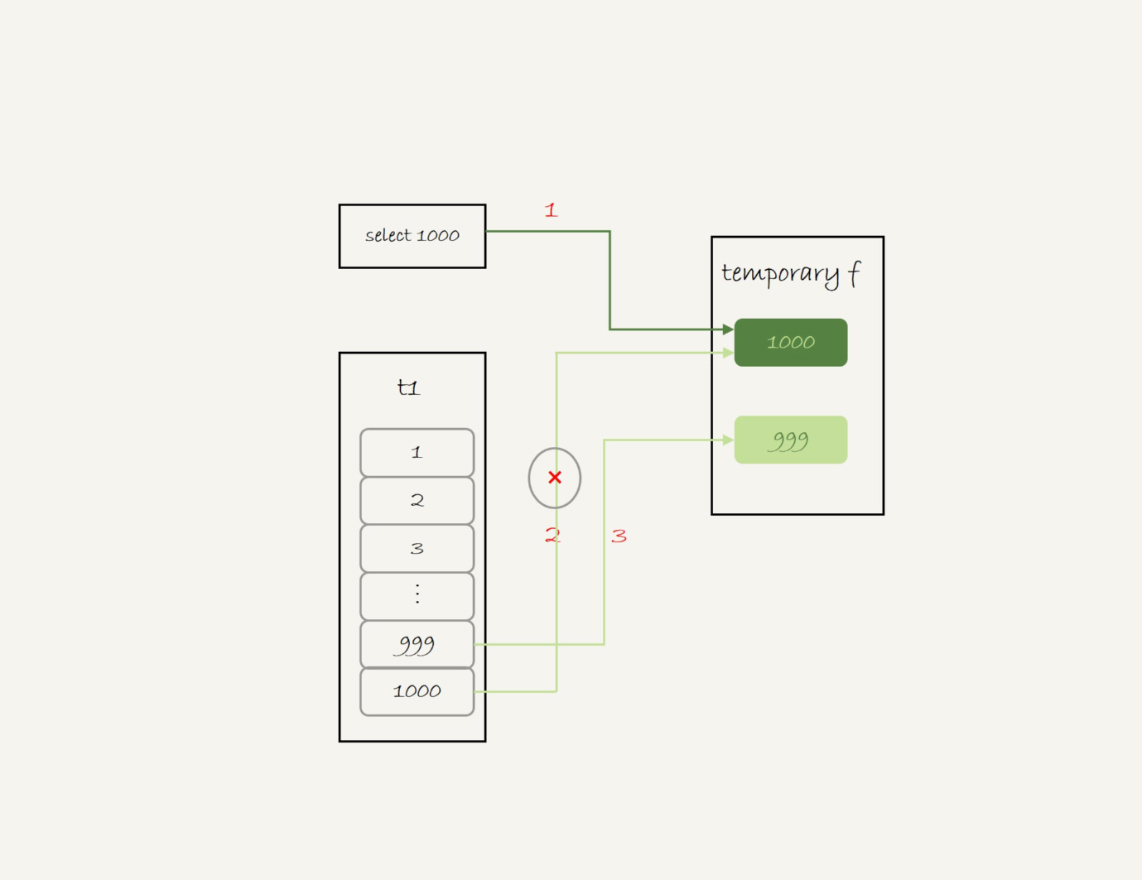
- 创建一个内存临时表,这个内存临时表只有一个整型字段f,并且f为主键
- 执行第一个子查询,得到1000,并存入内存临时表中
- 执行第二个子查询
- 拿到第一行id=1000,试图插入到内存临时表,但由于1000这个值已经存在于内存临时表
- 违反唯一性约束,插入失败,继续执行
- 拿到第二行id=999,插入内存临时表成功
- 拿到第一行id=1000,试图插入到内存临时表,但由于1000这个值已经存在于内存临时表
- 从内存临时表中按行取出数据,返回结果,并删除内存临时表,结果中包含id=1000和id=999两行
- 内存临时表起到了暂存数据的作用,还用到了内存临时表主键id的唯一性约束,实现union的语义
union all
union all没有去重的语义,一次执行子查询,得到的结果直接发给客户端,不需要内存临时表
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | mysql> explain ( select 1000 as f) union all ( select id from t1 order by id desc limit 2); + ----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | extra | + ----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------+ | 1 | primary | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | no tables used | | 2 | union | t1 | null | index | null | primary | 4 | null | 2 | 100.00 | backward index scan; using index | + ----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------+ |
group by
内存充足
?| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | -- 16777216 bytes = 16 mb mysql> show variables like '%tmp_table_size%' ; + ----------------+----------+ | variable_name | value | + ----------------+----------+ | tmp_table_size | 16777216 | + ----------------+----------+ |
执行语句
?| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 | -- mysql 5.6上执行 mysql> explain select id%10 as m, count (*) as c from t1 group by m; + ----+-------------+-------+-------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------------------------------------------+ | id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | extra | + ----+-------------+-------+-------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------------------------------------------+ | 1 | simple | t1 | index | primary ,a | a | 5 | null | 1000 | using index ; using temporary ; using filesort | + ----+-------------+-------+-------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------------------------------------------+ mysql> select id%10 as m, count (*) as c from t1 group by m; + ------+-----+ | m | c | + ------+-----+ | 0 | 100 | | 1 | 100 | | 2 | 100 | | 3 | 100 | | 4 | 100 | | 5 | 100 | | 6 | 100 | | 7 | 100 | | 8 | 100 | | 9 | 100 | + ------+-----+ |
using index:表示使用了覆盖索引,选择了索引a,不需要回表
using temporary:表示使用了临时表
using filesort:表示需要排序
执行过程
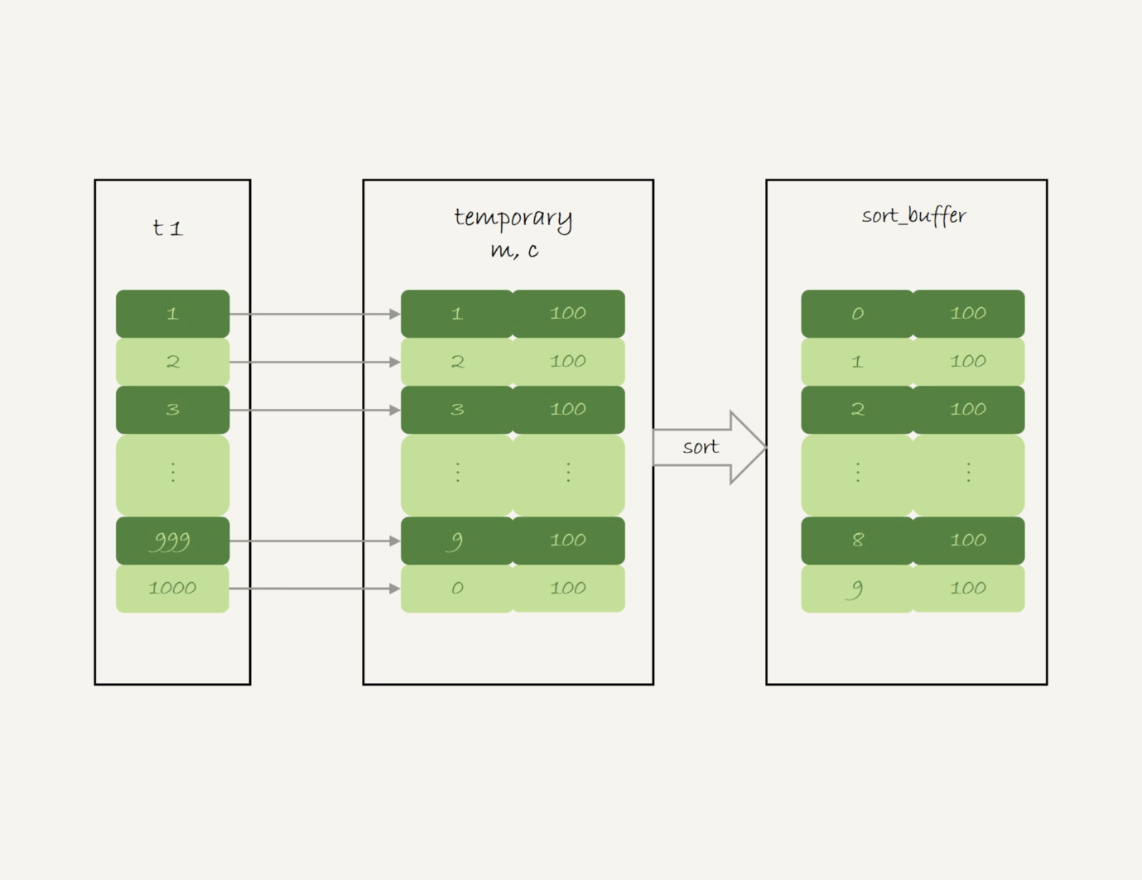
- 创建内存临时表,表里有两个字段m和c,m为主键
- 扫描t1的索引a,依次取出叶子节点上的id值,计算id%10,记为x
- 如果内存临时表中没有主键为x的行,插入一行记录
(x,1) - 如果内存临时表中有主键为x的行,将x这一行的c值加1
- 如果内存临时表中没有主键为x的行,插入一行记录
- 遍历完成后,再根据字段m做排序,得到结果集返回给客户端
排序过程
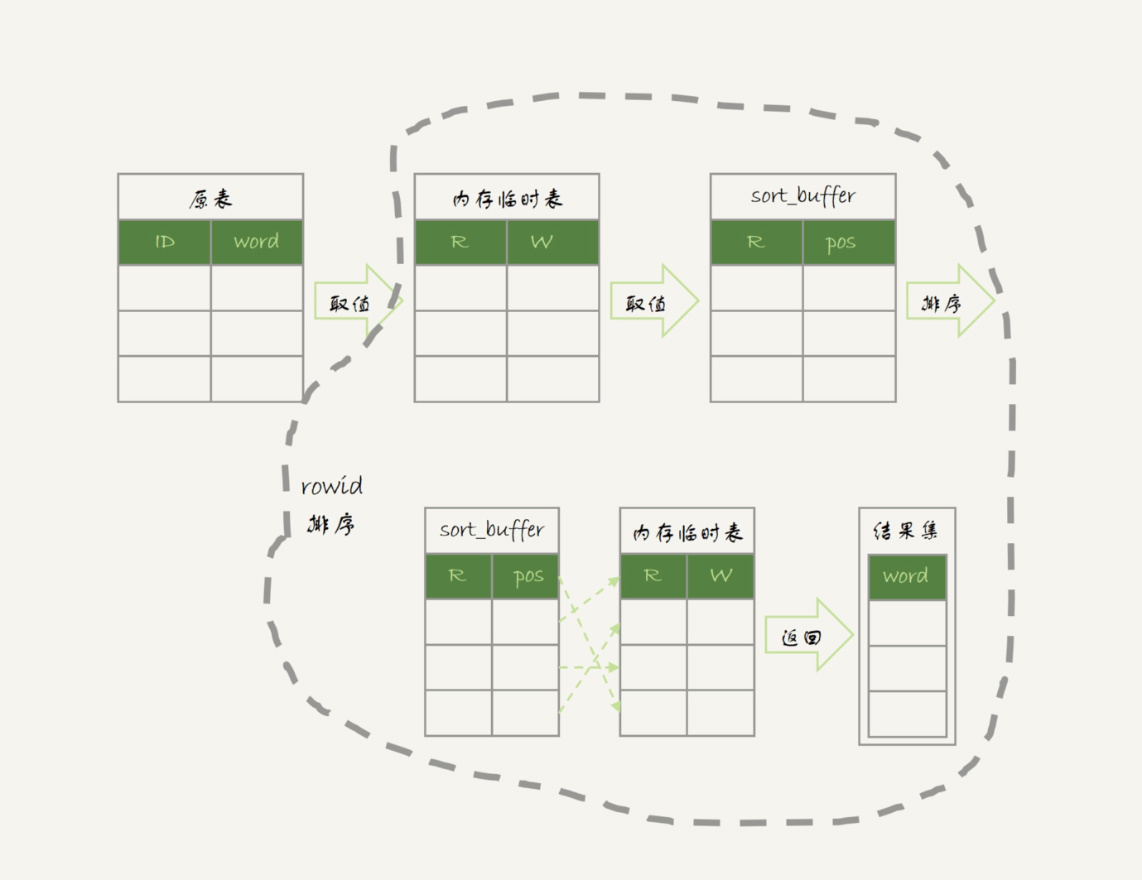
order by null
?| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 | -- 跳过最后的排序阶段,直接从临时表中取回数据 mysql> explain select id%10 as m, count (*) as c from t1 group by m order by null ; + ----+-------------+-------+-------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+------------------------------+ | id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | extra | + ----+-------------+-------+-------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+------------------------------+ | 1 | simple | t1 | index | primary ,a | a | 5 | null | 1000 | using index ; using temporary | + ----+-------------+-------+-------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+------------------------------+ -- t1中的数据是从1开始的 mysql> select id%10 as m, count (*) as c from t1 group by m order by null ; + ------+-----+ | m | c | + ------+-----+ | 1 | 100 | | 2 | 100 | | 3 | 100 | | 4 | 100 | | 5 | 100 | | 6 | 100 | | 7 | 100 | | 8 | 100 | | 9 | 100 | | 0 | 100 | + ------+-----+ |
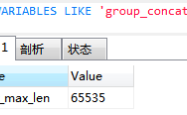
内存不足
?| 1 | set tmp_table_size=1024; |
执行语句
?| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 | -- 内存临时表的上限为1024 bytes,但内存临时表不能完全放下100行数据,内存临时表会转成磁盘临时表,默认采用innodb引擎 -- 如果t1很大,这个查询需要的磁盘临时表就会占用大量的磁盘空间 mysql> select id%100 as m, count (*) as c from t1 group by m order by null limit 10; + ------+----+ | m | c | + ------+----+ | 1 | 10 | | 2 | 10 | | 3 | 10 | | 4 | 10 | | 5 | 10 | | 6 | 10 | | 7 | 10 | | 8 | 10 | | 9 | 10 | | 10 | 10 | + ------+----+ |
优化方案
优化索引
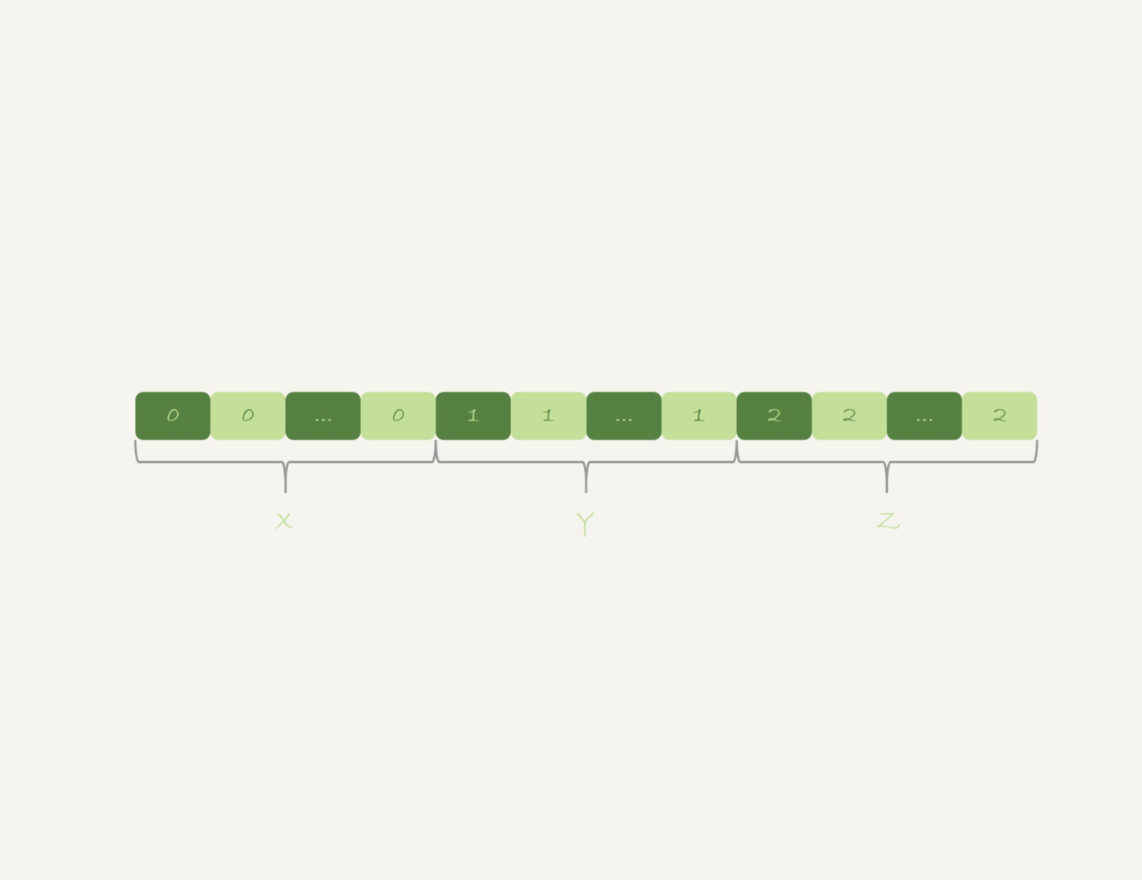
不论使用内存临时表还是磁盘临时表,group by都需要构造一个带唯一索引的表,执行代价较高
需要临时表的原因:每一行的id%100是无序的,因此需要临时表,来记录并统计结果
如果可以确保输入的数据是有序的,那么计算group by时,只需要
从左到右顺序扫描,依次累加即可
- 当碰到第一个1的时候,已经累积了x个0,结果集里的第一行为
(0,x) - 当碰到第一个2的时候,已经累积了y个1,结果集里的第一行为
(1,y) - 整个过程不需要临时表,也不需要排序
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | -- mysql 5.7上执行 alter table t1 add column z int generated always as (id % 100), add index (z); -- 使用了覆盖索引,不需要临时表,也不需要排序 mysql> explain select z, count (*) as c from t1 group by z; + ----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | extra | + ----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+ | 1 | simple | t1 | null | index | z | z | 5 | null | 1000 | 100.00 | using index | + ----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+ 2 |
直接排序
一个group by语句需要放到临时表的数据量特别大,还是按照先放在内存临时表,再退化成磁盘临时表
可以直接用磁盘临时表的形式,在group by语句中sql_big_result(告诉优化器涉及的数据量很大)
磁盘临时表原本采用b+树存储,存储效率还不如数组,优化器看到sql_big_result,会直接用数组存储
- 即放弃使用临时表,直接进入排序阶段
执行过程
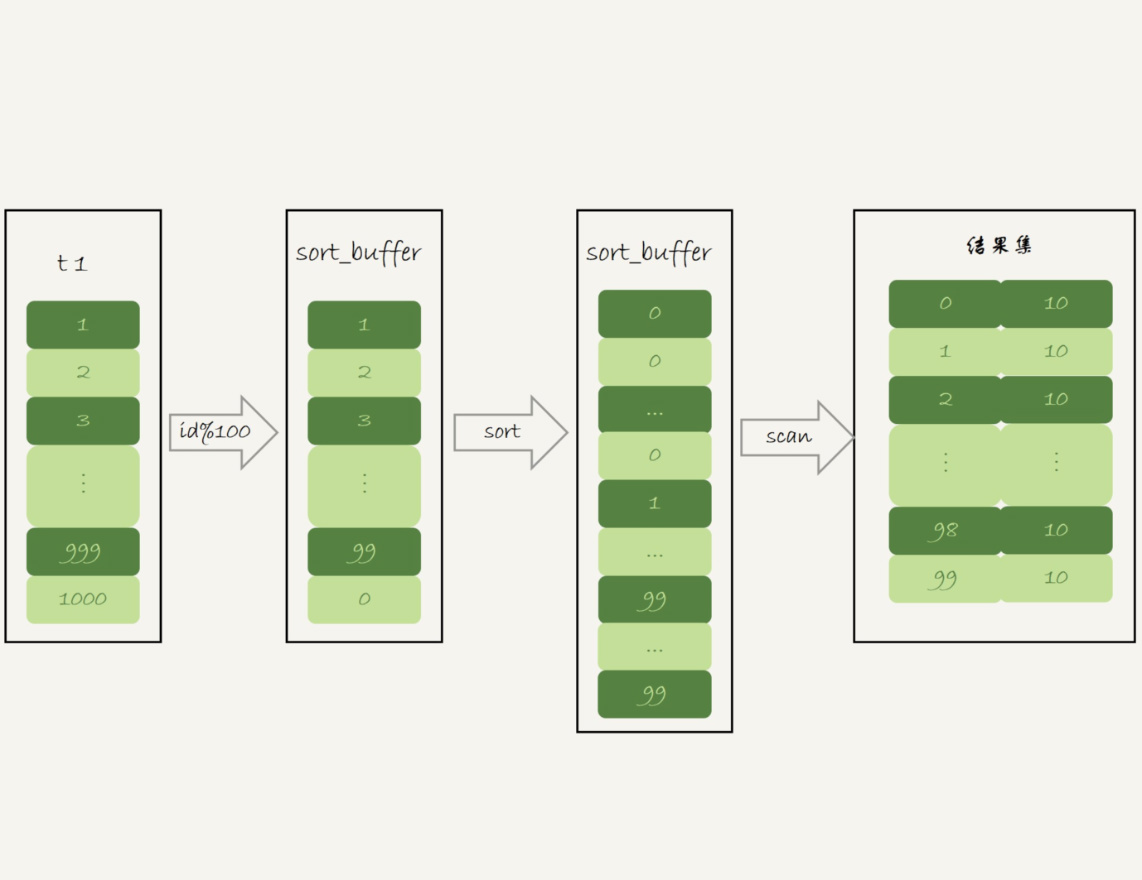
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | -- 没有再使用临时表,而是直接使用了排序算法 mysql> explain select sql_big_result id%100 as m, count (*) as c from t1 group by m; + ----+-------------+-------+-------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+-----------------------------+ | id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | extra | + ----+-------------+-------+-------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+-----------------------------+ | 1 | simple | t1 | index | primary ,a | a | 5 | null | 1000 | using index ; using filesort | + ----+-------------+-------+-------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+-----------------------------+ |
初始化sort_buffer,确定放入一个整型字段,记为m
扫描t1的索引a,依次取出里面的id值,将id%100的值放入sort_buffer
扫描完成后,对sort_buffer的字段m做排序(sort_buffer内存不够时,会利用磁盘临时文件辅助排序)
排序完成后,得到一个有序数组,遍历有序数组,得到每个值出现的次数(类似上面优化索引的方式)
对比distinct
?| 1 2 3 4 5 6 | -- 标准sql,select部分添加一个聚合函数count(*) select a, count (*) from t group by a order by null ; -- 非标准sql select a from t group by a order by null ; select distinct a from t; |
标准sql:按照字段a分组,计算每组a出现的次数
非标准sql:没有了count(*),不再需要执行计算总数的逻辑
- 按照字段a分组,相同的a的值只返回一行,与
distinct语义一致
如果不需要执行聚合函数 ,distinct和group by的语义、执行流程和执行性能是相同的
- 创建一个临时表,临时表有一个字段a,并且在这个字段a上创建一个唯一索引
- 遍历表t,依次取出数据插入临时表中
- 如果发现唯一键冲突,就跳过
- 否则插入成功
- 遍历完成后,将临时表作为结果集返回给客户端
小结
- 用到内部临时表的场景
- 如果语句执行过程中可以一边读数据,一边得到结果,是不需要额外内存的
- 否则需要额外内存来保存中间结果
-
join_buffer是无序数组,sort_buffer是有序数组,临时表是二维表结构 - 如果执行逻辑需要用到二维表特性,就会优先考虑使用临时表如果对
group by语句的结果没有明确的排序要求,加上order by null(mysql 5.6) - 尽量让
group by过程用上索引,确认explain结果没有using temporary和using filesort - 如果
group by需要统计的数据量不大,尽量使用内存临时表(可以适当调大tmp_table_size) - 如果数据量实在太大,使用
sql_big_result来告诉优化器直接使用排序算法(跳过临时表)
参考资料
《mysql实战45讲》
到此这篇关于mysql内部临时表的具体使用的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关mysql内部临时表内容请搜索服务器之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持服务器之家!
原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/yungyu16/p/12961696.html
1.本站遵循行业规范,任何转载的稿件都会明确标注作者和来源;2.本站的原创文章,请转载时务必注明文章作者和来源,不尊重原创的行为我们将追究责任;3.作者投稿可能会经我们编辑修改或补充。