MySQL预编译功能详解
本文为大家分享了MySQL预编译功能,供大家参考,具体内容如下
1、预编译的好处
大家平时都使用过JDBC中的PreparedStatement接口,它有预编译功能。什么是预编译功能呢?它有什么好处呢?
当客户发送一条SQL语句给服务器后,服务器总是需要校验SQL语句的语法格式是否正确,然后把SQL语句编译成可执行的函数,最后才是执行SQL语句。其中校验语法,和编译所花的时间可能比执行SQL语句花的时间还要多。
如果我们需要执行多次insert语句,但只是每次插入的值不同,MySQL服务器也是需要每次都去校验SQL语句的语法格式,以及编译,这就浪费了太多的时间。如果使用预编译功能,那么只对SQL语句进行一次语法校验和编译,所以效率要高。
2、MySQL执行预编译
MySQL执行预编译分为如三步:
执行预编译语句,例如:prepare myfun from 'select * from t_book where bid=?'
设置变量,例如:set @str='b1'
执行语句,例如:execute myfun using @str
如果需要再次执行myfun,那么就不再需要第一步,即不需要再编译语句了:
设置变量,例如:set @str='b2'
执行语句,例如:execute myfun using @str
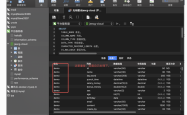
通过查看MySQL日志可以看到执行的过程:
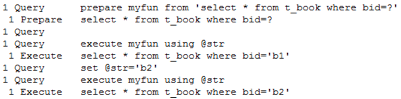
3、使用Statement执行预编译
使用Statement执行预编译就是把上面的SQL语句执行一次。
?| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 | Connection con = JdbcUtils.getConnection(); Statement stmt = con.createStatement(); stmt.executeUpdate( "prepare myfun from 'select * from t_book where bid=?'" ); stmt.executeUpdate( "set @str='b1'" ); ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery( "execute myfun using @str" ); while(rs. next ()) { System. out .print(rs.getString(1) + ", " ); System. out .print(rs.getString(2) + ", " ); System. out .print(rs.getString(3) + ", " ); System. out .println(rs.getString(4)); } stmt.executeUpdate( "set @str='b2'" ); rs = stmt.executeQuery( "execute myfun using @str" ); while(rs. next ()) { System. out .print(rs.getString(1) + ", " ); System. out .print(rs.getString(2) + ", " ); System. out .print(rs.getString(3) + ", " ); System. out .println(rs.getString(4)); } rs. close (); stmt. close (); con. close (); |
4、useServerPrepStmts参数
默认使用PreparedStatement是不能执行预编译的,这需要在url中给出useServerPrepStmts=true参数(MySQL Server
4.1之前的版本是不支持预编译的,而Connector/J在5.0.5以后的版本,默认是没有开启预编译功能的)。
例如:jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?useServerPrepStmts=true
这样才能保证mysql驱动会先把SQL语句发送给服务器进行预编译,然后在执行executeQuery()时只是把参数发送给服务器。
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 | Connection con = JdbcUtils.getConnection(); String sql = "select * from t_book where bid=?" ; PreparedStatement pstmt = con.prepareStatement(sql); pstmt.setString( 1 , "b1" ); ResultSet rs = pstmt.executeQuery(); while (rs.next()) { System.out.print(rs.getString( 1 ) + ", " ); System.out.print(rs.getString( 2 ) + ", " ); System.out.print(rs.getString( 3 ) + ", " ); System.out.println(rs.getString( 4 )); } pstmt.setString( 1 , "b2" ); rs = pstmt.executeQuery(); while (rs.next()) { System.out.print(rs.getString( 1 ) + ", " ); System.out.print(rs.getString( 2 ) + ", " ); System.out.print(rs.getString( 3 ) + ", " ); System.out.println(rs.getString( 4 )); } rs.close(); pstmt.close(); con.close(); |
5、cachePrepStmts参数
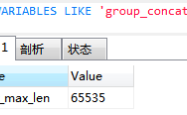
当使用不同的PreparedStatement对象来执行相同的SQL语句时,还是会出现编译两次的现象,这是因为驱动没有缓存编译后的函数key,导致二次编译。如果希望缓存编译后函数的key,那么就要设置cachePrepStmts参数为true。例如:
jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?useServerPrepStmts=true&cachePrepStmts=true
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 | Connection con = JdbcUtils.getConnection(); String sql = "select * from t_book where bid=?" ; PreparedStatement pstmt = con.prepareStatement(sql); pstmt.setString( 1 , "b1" ); ResultSet rs = pstmt.executeQuery(); while (rs.next()) { System.out.print(rs.getString( 1 ) + ", " ); System.out.print(rs.getString( 2 ) + ", " ); System.out.print(rs.getString( 3 ) + ", " ); System.out.println(rs.getString( 4 )); } pstmt = con.prepareStatement(sql); pstmt.setString( 1 , "b2" ); rs = pstmt.executeQuery(); while (rs.next()) { System.out.print(rs.getString( 1 ) + ", " ); System.out.print(rs.getString( 2 ) + ", " ); System.out.print(rs.getString( 3 ) + ", " ); System.out.println(rs.getString( 4 )); } rs.close(); pstmt.close(); con.close(); |
6、打开批处理
MySQL的批处理也需要通过参数来打开:rewriteBatchedStatements=true
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持服务器之家。
原文链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/gdwkong/archive/2017/10/07/7635541.html
1.本站遵循行业规范,任何转载的稿件都会明确标注作者和来源;2.本站的原创文章,请转载时务必注明文章作者和来源,不尊重原创的行为我们将追究责任;3.作者投稿可能会经我们编辑修改或补充。