进程状态ps -ef中的e、f含义讲解
linux或mac控制台下输入ef="/office/226150.html">ps -ef | grep 关键字可以查看是否有相应的进程启动信息中包含关键字。如:
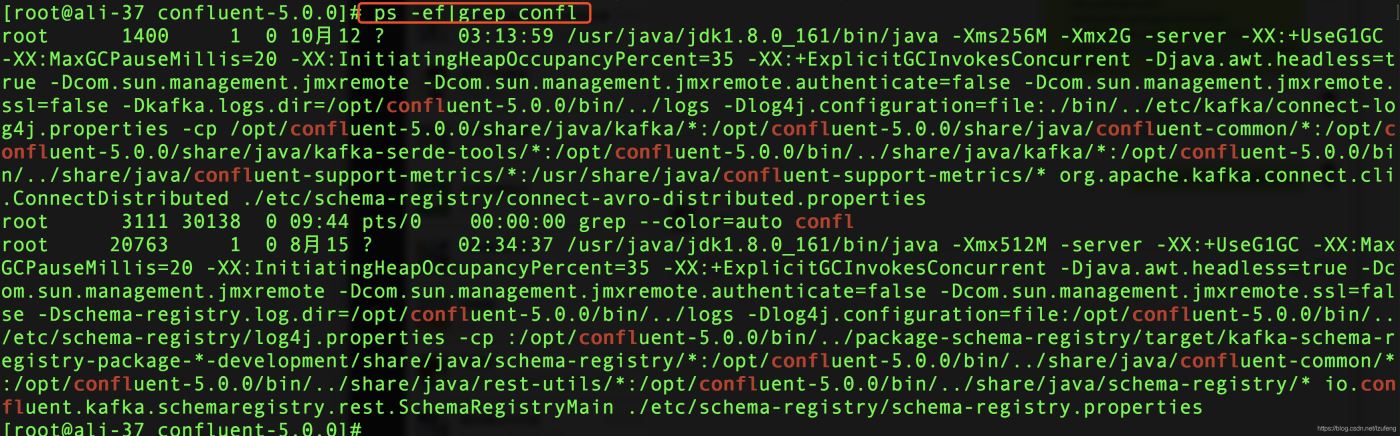
ps的意思是process status,即进程状态。在控制台执行man ps命令可以查看ps命令后面的命令选项的含义如下:
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 | The options are as follows: -A Display information about other users' processes, including those without controlling ter- minals. -a Display information about other users' processes as well as your own. This will skip any processes which do not have a controlling terminal, unless the -x option is also specified. -C Change the way the CPU percentage is calculated by using a ``raw'' CPU calculation that ignores ``resident'' time (this normally has no effect). -c Change the ``command'' column output to just contain the executable name, rather than the full command line. -d Like -A, but excludes session leaders. -E Display the environment as well. This does not reflect changes in the environment after process launch. -e Identical to -A. -f Display the uid, pid, parent pid, recent CPU usage, process start time, controlling tty, elapsed CPU usage, and the associated command. If the -u option is also used, display the user name rather then the numeric uid. When -o or -O is used to add to the display follow- ing -f, the command field is not truncated as severely as it is in other formats. -G Display information about processes which are running with the specified real group IDs. -g Display information about processes with the specified process group leaders. -h Repeat the information header as often as necessary to guarantee one header per page of information. -j Print information associated with the following keywords: user, pid, ppid, pgid, sess, jobc, state, tt, time, and command. -L List the set of keywords available for the -O and -o options. -l Display information associated with the following keywords: uid, pid, ppid, flags, cpu, pri, nice, vsz=SZ, rss, wchan, state=S, paddr=ADDR, tty, time, and command=CMD. -M Print the threads corresponding to each task. -m Sort by memory usage, instead of the combination of controlling terminal and process ID. -O Add the information associated with the space or comma separated list of keywords speci- fied, after the process ID, in the default information display. Keywords may be appended with an equals (`=') sign and a string. This causes the printed header to use the speci- fied string instead of the standard header. -o Display information associated with the space or comma separated list of keywords speci- fied. Multiple keywords may also be given in the form of more than one -o option. Key- words may be appended with an equals (`=') sign and a string. This causes the printed header to use the specified string instead of the standard header. If all keywords have empty header texts, no header line is written. -p Display information about processes which match the specified process IDs. -r Sort by current CPU usage, instead of the combination of controlling terminal and process ID. -S Change the way the process time is calculated by summing all exited children to their par- ent process. -T Display information about processes attached to the device associated with the standard input. -t Display information about processes attached to the specified terminal devices. -U Display the processes belonging to the specified real user IDs. -u Display the processes belonging to the specified usernames. -v Display information associated with the following keywords: pid, state, time, sl, re, pagein, vsz, rss, lim, tsiz, %cpu, %mem, and command. The -v option implies the -m option. -w Use 132 columns to display information, instead of the default which is your window size. If the -w option is specified more than once, ps will use as many columns as necessary without regard for your window size. When output is not to a terminal, an unlimited number of columns are always used. -X When displaying processes matched by other options, skip any processes which do not have a controlling terminal. -x When displaying processes matched by other options, include processes which do not have a controlling terminal. This is the opposite of the -X option. If both -X and -x are speci- fied in the same command, then ps will use the one which was specified last. |
可见
-e和-A的意思是一样的,即显示有关其他用户进程的信息,包括那些没有控制终端的进程。
-f显示用户id,进程id,父进程id,最近CPU使用情况,进程开始时间等等。
ps -ef命令含义
工作中,平时都是通过ps -ef 去进行查看系统上的运行的所有进程,是一个特别常用的命令;这里说下该命令的具体含义:
只执行ps命令,默认是显示当前控制台下属于当前用户的进程;
参数 -e 显示运行在系统上的所有进程
参数 -f 扩展显示输出
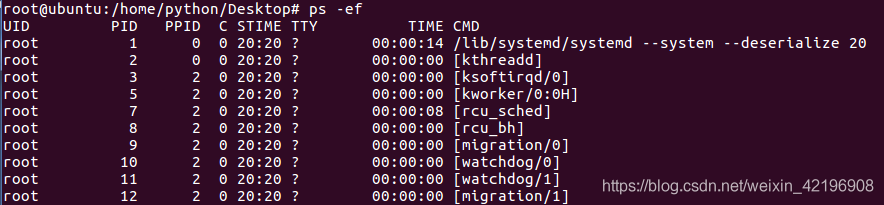
UID 启动进程的用户
PID 进程的进程号
PPID 父进程进程号
C cpu使用率
STIME 进程启动时的系统时间
TTY 进程启动时终端设备
TIME 运行进程需要的累积CPU时间
CMD 启动程序名称或命令
更多的ps命令可以通过 man ps 或者 ps --help all 来获取
到此这篇关于进程状态ps -ef中的e、f含义讲解的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关ps -ef中e、f含义内容请搜索服务器之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持服务器之家!
原文链接:https://manongwushuang.blog.csdn.net/article/details/83537275
1.本站遵循行业规范,任何转载的稿件都会明确标注作者和来源;2.本站的原创文章,请转载时务必注明文章作者和来源,不尊重原创的行为我们将追究责任;3.作者投稿可能会经我们编辑修改或补充。