mysql中left join设置条件在on与where时的用法区别分析
本文实例讲述了mysql中left join设置条件在on与where时的用法区别。分享给大家供大家参考,具体如下:
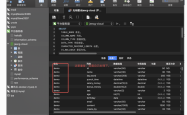
一、首先我们准备两张表来进行测试。
?| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | create table `a` ( `id` int (11) unsigned not null auto_increment comment 'id' , ` name ` varchar (32) default '' comment '名称' , primary key (`id`) ) engine=innodb default charset=utf8; create table `b` ( `id` int (11) unsigned not null auto_increment comment 'id' , `a_id` int (11) default '0' comment 'a表id' , ` name ` varchar (32) default '' comment '名称' , primary key (`id`) ) engine=innodb default charset=utf8; |
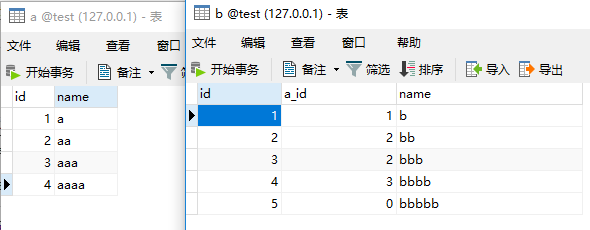
两个表的数据如图所示:
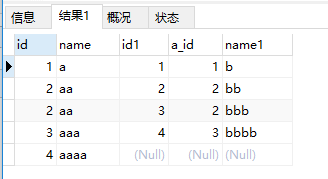
运行下面左连接查询:
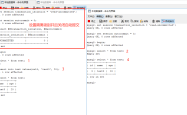
?| 1 | select * from a left join b on a.id = b.a_id; |
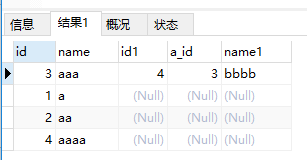
我们分别在on和where后面加上条件,看看执行结果是否相同。
?| 1 | select * from a left join b on a.id = b.a_id and b.id > 3; |
| 1 | select * from a left join b on a.id = b.a_id where b.id > 3; |
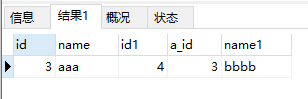
上面的两条语句,条件我们设置的是一样的都是b.id > 3,为什么显示结果不同。
sql语句查询的关键字顺序一般为 from > where > group by > having > order by
left join 在 from范围,on 条件会先对 left join 的右表进行筛选,筛选完后的结果 where 再进行筛选。
多个 left join 会生成一张临时表,on 条件是对 left join 右表进行条件过滤,where 条件针对最后生成的临时表进行过滤。
所以:
b.id > 3 的条件如果写在 on 后面,则是先对右边表(关联表)进行筛选,得出符合条件的行,然后主表 left join ,返回主表所有的行,右边表没匹配上的用 null 表示。
b.id > 3 的条件如果写在 where 后面,则是先主表 left join 右边表(关联表),返回所有的行,然后 where 条件再对结果进行筛选。
注意:on 后面的条件是针对右边的表(关联表),对主表没什么作用。
?| 1 | select * from a left join b on a.id = b.a_id and a.id > 3; |
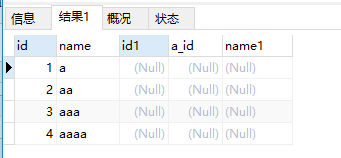
我们在on 后面添加了对主表的条件 a.id > 3,不过主表的数据仍然全部显示出来了,但是影响了右边表(关联表)的显示。
如果想要对主表进行筛选,应该把条件写在where后。
?| 1 | select * from a left join b on a.id = b.a_id where a.id > 3; |
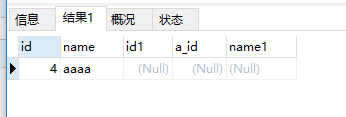
希望本文所述对大家MySQL数据库计有所帮助。
原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/jkko123/p/10148927.html
1.本站遵循行业规范,任何转载的稿件都会明确标注作者和来源;2.本站的原创文章,请转载时务必注明文章作者和来源,不尊重原创的行为我们将追究责任;3.作者投稿可能会经我们编辑修改或补充。