MySQL 使用DQL命令查询数据的实现方法
本篇文章博主将带大家一起学习mysql中常用的数据查询语言。
dql(data query language 数据查询语言)
select 语法
?| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | select [ all | distinct ] { * | table .* | [ table .field1 [ as alias1][, table .field2] [ as alias2][,...]]} from table_name [ as table_alias] [ left | out | inner join table_name2] #联合查询 [ where ...] #指定结果需要满足的条件 [ group by ...] #指定结果按照哪几个字段来分组 [ having ...] #过滤分组的记录必须满足的次要条件 [oder by ...] #指定查询记录按一个或者多个条件排序 [limit [偏移量,返回结果记录数]; #指定查询的记录从哪条至哪条 |
基本查询语句&as
以下例子用student表中的数据。


查询表中所有数据列结果,采用 “*” 符号,效率低
?| 1 | select * from student; |
可指定查询列,效率高
?| 1 | select studentname,phone from student; |
as 子句的作用和用法
注意:as 可省略不写
(1)可给数据列取一个新别名
?| 1 | select studentname as '学生姓名' from student; |
(2)给表取别名
?| 1 | select stu.address from student as stu; |
(3)可把计算或总结的结果用另一个新名称来代替
?| 1 | select phone +1 as tel from student; |
distinct 关键字
作用:去掉select查询出来的重复值(当所有返回值都相同时,只返回一条记录)
语法:
?| 1 | select distinct 字段名1,字段名2,... from 表名 |
注意:all 关键字是默认的,返回所有记录,与之相反
当过滤多列重复值时,只有当选择过滤的列都存在重复值才进行过滤
?| 1 | select distinct studentno,address from student; |
过滤单列:查询学生表中的地址
?| 1 | select distinct address from student; |
sql语句中的表达式
?| 1 2 3 | select version(),100*3 as 乘积; #返回mysql 版本和计算结果 select now() '当前时间' ; #返回当前时间 |


避免sql返回结果中包含“.” ,“*”,和括号等干扰开发语言程序
?| 1 2 | select version() as mysql_v,12.3*100 as expression; #返回结果不会与后台开发程序发生混淆 |
拼接 concat
?| 1 | select concat(studentname, '@.com' ) as email from student; |
数值类型相加
?| 1 | select studentno+100 from student; |
比较运算符&通配符
where条件语句:用于检索数据表中符合条件的记录
搜索条件可以由一个或多个逻辑表达式组成,结果一般为真或假
搜索条件的组成:逻辑操作符、比较操作符
?| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | # where 条件语句 select * from student where address= '四川' ; #查询学生表中电话号码不为空的学员姓名 select studentname from student where phone is not null ; #查询学生表中电话号码为空的学员姓名 select studentname from student where phone is null ; #查询刚删掉的数据——空值 select studentname from student where phone = '' ; # between and 适用于时间范围 |
逻辑操作符

比较操作符

使用 like 关键字进行模糊查询
- 与“%”一起使用,表示匹配0个或任意个字符
- 与“_”一起使用 表示匹配单个字符
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 | #查询学生表中姓张*的学生姓名 select studentname from student where studentname like '张_' ; select studentname from student where studentname like '%丽%' ; # in select * from student where address in ( '四川' , '上海' ); |
注意:
- 数值数据类型的记录之间才能进行算数运算
- 相同的数据类型的数据之间才能进行比较
null
- null 代表“无值”
- 区别于零值0和空字符串“ ”
- 只能出现在定义允许为null的字段
- 须使用 is null 或 is not null 比较操作符去比较
内连接&自查询
如果需要多张数据表的数据进行查询,则可以通过连接运算符实现多个查询。
分类包括:
- 内连接(inner jion):
- 等值和非等值的连接查询
- 自身连接查询
- 外连接(out jion)
- 左连接(left jion)
- 右连接(right jion)
order by 排序查询
对select 语句查询得到的结果,按某些字段进行排序
与desc(降序)或asc(升序)搭配使用,默认为asc
以subject表和grade表数据为例:


| 1 2 | select * from subject order by classhour; #升序 select * from subject order by classhour desc ; #降序 |
多字段排序:先按照第一个字段排序,再按照第二个字段排序。如果第一个字段数据相同,再按照第二个字段排序。
?| 1 | select * from subject order by classhour,gradeid; |

limit分页
limit [m,] n 或 limit n offset m
限制select返回结果的行数
m为第一个返回记录行的偏移量
n返回记录行的数目
注意:
- m不指定,则偏移量为0,从第一条开始返回前n条记录
- limit 常用于分页显示
- 如果超出表中数据,则显示全部
例如:
?| 1 2 | select * from grade limit 3; #返回前3条记录 select * from grade limit 1,3; #返回2~4条记录 |


总记录数:total
?| 1 | select count (subjectno) '总数据' from subject; |

总页数:int totalpage = total % pagesize ==0 ? total / pagesize : total / pagesize + 1
子查询
在查询语句where 条件子句中,又嵌套了另外一个查询语句
注意:子查询返回的结果一般是集合,建议使用in关键字
?| 1 2 3 | select subjectname from subject where gradeid in ( select gradeid from grade); |

聚合函数
常用的统计函数:count()、sum()、avg()、max()、min()
?| 1 2 3 4 5 | select count (studentno) '总数据' from student; select sum (classhour) '总学时' from subject; select avg (classhour) '平均学时' from subject; select max (classhour) '最长学时' from subject; select min (classhour) '最短学时' from subject; |
分组 group by
使用 group by 关键字对查询结果分组
- 对所有的数据进行分组统计
- 分组的字段可以有多个,并依次分组
- 与 having 结合使用,进行分组后的数据筛选
以 student 表为例

(1)对student 表按照地址分组统计 group by
?| 1 | select address, count (address) from student group by address; |

having 过滤分组的记录必须满足的次要条件
(2)对 student 表 按照地址分组,满足地址=1的 having
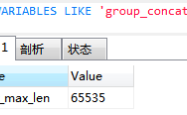
?| 1 | select group_concat(studentname), count (address) from student group by address having count (address)=1; |

合并 union 、union
- allunion #合并完全相同数据
- union all #合并所有数据
注意:合并两张表时,列数必须一样才能合并。
两表列数不同时,会报以下错误:
[sql]select * from grade union select * from student;
[err] 1222 - the used select statements have a different number of columns
(1)合并 subject 表和 student表
?| 1 2 | select * from subject union select * from student; select * from subject union all select * from student; |

子查询 exists ——>true false
exists / not exists 子查询条件成立则显示父查询的结果,否则不显示结果
(1)子查询条件为真 (grade 表中 gradeid 1~5,存在 1)
?| 1 2 3 | select subjectname,gradeid from subject where exists ( select * from grade where gradeid=1); |
或
?| 1 2 3 | select subjectname,gradeid from subject where not exists ( select * from grade where gradeid=999); |

(2)子查询条件为假 (grade 表中 gradeid 1~5,不存在 999)
?| 1 2 3 | select subjectname,gradeid from subject where exists ( select * from grade where gradeid=999); |
或
?| 1 2 3 | select subjectname,gradeid from subject where not exists ( select * from grade where gradeid=1); |

子查询(any & all)
any :判断条件中,若子查询中任意一个值满足条件,则执行父查询
all :判断条件中,若子查询中所有值满足条件,则执行父查询
(1)满足条件:存在 subject.gradeid >= grade.gradeid ,执行父查询
| 1 2 3 | select subjectname,gradeid from subject where gradeid >= any ( select gradeid from grade); |

(2)不满足条件:所有subject.gradeid >= grade.gradeid ,不执行父查询
?| 1 2 3 | select subjectname,gradeid from subject where gradeid >= all ( select gradeid from grade); |

以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持服务器之家。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43817064/article/details/97936194
1.本站遵循行业规范,任何转载的稿件都会明确标注作者和来源;2.本站的原创文章,请转载时务必注明文章作者和来源,不尊重原创的行为我们将追究责任;3.作者投稿可能会经我们编辑修改或补充。